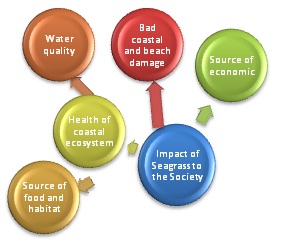
 Seagrass are flowering plants found in shallow marine waters. A vital part of the marine ecosystem due to their productivity level, seagrass provide food, habitat and nursery areas for numerous vertebrate and invertebrate species. The vast biodiversity and sensitivity to changes in water quality inherent in seagrass communities makes seagrasses an important species to help determine the overall health of coastal ecosystems. Seagrasses perform numerous functions in stabilizing the sea bottom, providing food and habitat for other marine organisms, maintaining water quality and supporting local economies.
Seagrass are flowering plants found in shallow marine waters. A vital part of the marine ecosystem due to their productivity level, seagrass provide food, habitat and nursery areas for numerous vertebrate and invertebrate species. The vast biodiversity and sensitivity to changes in water quality inherent in seagrass communities makes seagrasses an important species to help determine the overall health of coastal ecosystems. Seagrasses perform numerous functions in stabilizing the sea bottom, providing food and habitat for other marine organisms, maintaining water quality and supporting local economies.
1. Prevent damage to ocean and beach area
Seagrasses are plants that have extensive root system vertically and horizontally. These roots can prevent the soil erosion by stabilizing the sea bottom. As for ocean 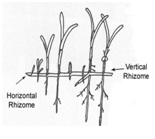 bottom areas with no seagrasses, the force of currents and the intense of wave action will give bad impact to the beaches and the ocean. Seagrasses, with their extensive root systems, act to stabilize and trap bottom sediments thereby providing protection against erosion. Furthermore, seagrass help in natural treats to the climate change such preventing from droughts and floods that can change the water salinity. Thus, this will also effect to the fishermen and tourism society.
bottom areas with no seagrasses, the force of currents and the intense of wave action will give bad impact to the beaches and the ocean. Seagrasses, with their extensive root systems, act to stabilize and trap bottom sediments thereby providing protection against erosion. Furthermore, seagrass help in natural treats to the climate change such preventing from droughts and floods that can change the water salinity. Thus, this will also effect to the fishermen and tourism society.
2. Water quality to environment
Seagrasses become beds in improving water quality where when the water from the river flew into the sea, they carry fresh water, silts and chemicals. The seagrass roots and blades will trap, filter and recycle the excess nutrients that contain phosphorus and nitrogen and change them to food for the organisms in the water. Seagrass also play it rolls in mixing the fresh water and salts water before reaching the reef so that it maintain the suitable salinity for the ocean living things. Therefore, seagrass help in maintaining a good water quality and prevent from water pollutant.
3. Source of food and habitat
Reef animals come to seagrass bed to mate, hiding from enemies, lay eggs and become nursery for animals. Only some animals can digest the seagrass’s blade such as some fish, sea tutles and dugongs and find food (organism) in the bunch of seagrass area. These two scenarios are important for maintaining the biodiversity, life cycles and wide range of life in the ocean. Thus, local communities will enjoy seeing the beautiful ocean nature during their snorkeling and scuba diving. Therefore, it is critically important to estimate seagrass biomass for sustainability.
4. Supporting local economic
 Seagrass can be an ingredient for many product such as toothpaste and food product like ice creams and crackers and craft such as seagrass basket. These become the way for fishers to earn income by harvesting and selling seagrasses to the suitable sectors and produce such product. Furthermore, seagrass also valued to aquarium landscape for aquarium hobbyists that becomes people attractions. Thus, this will effect to the industrial sector.
Seagrass can be an ingredient for many product such as toothpaste and food product like ice creams and crackers and craft such as seagrass basket. These become the way for fishers to earn income by harvesting and selling seagrasses to the suitable sectors and produce such product. Furthermore, seagrass also valued to aquarium landscape for aquarium hobbyists that becomes people attractions. Thus, this will effect to the industrial sector.
Seagrass meadows are like underwater lawns. But more than just being nice-looking, they play important ecological and environmental roles. These carpet of green and lush leaves have a special relationship with many marine animals by providing food and shelter. The largest animals associated with seagrasses in the Caribbean are the endangered Green sea turtle and the Caribbean manatee.
In addition, seagrasses provide environmental services to people by helping to clean water by absorbing harmful chemicals and nutrients. Seagrasses protect the coastlines by weakening wave energy. Seagrass stabilize sediments so they also make it easy for dust bits to settle at the bottom. And last but not least, much of the seaweed you see washed up on the beach is dead seagrass that brings good nutrients to the beach and help to form dunes.
Threats to Seagrasses
The most important threats to seagrasses are damages from boat anchors, pollution and dredging. Anchoring destroys the seagrass beds by uprooting them. When roots are damaged, the plants die. There are all types of pollution that can affect seagrasses, some invisible and some visible. Dredging can directly or indirectly impact seagrass habitats. Stay informed about dredging activities in your area and support measures to protect seagrass during these operations. Chemicals, sometimes invisible, can kill the plants from inside out when the plants absorb the harmful substances. But also pollution like plastic bags can also kill seagrasses.
beds by uprooting them. When roots are damaged, the plants die. There are all types of pollution that can affect seagrasses, some invisible and some visible. Dredging can directly or indirectly impact seagrass habitats. Stay informed about dredging activities in your area and support measures to protect seagrass during these operations. Chemicals, sometimes invisible, can kill the plants from inside out when the plants absorb the harmful substances. But also pollution like plastic bags can also kill seagrasses.
When a plastic bag covers a grass patch, sunlight cannot reach the grass and they die. Dredging is usually done to make the water deeper for the purpose of ship traffic. Dredging makes the water very cloudy with lots of bits of soil particles. This is called particle suspension. When these bits of soil eventually fall to the bottom, a process called sedimentation, the thick blanket of sediment covers and suffocates the grasses. Both particle suspension and heavy sedimentation prevent sunlight from reaching the grasses.
Reference:
- Marine Life. About.com. 2014. “Seagrasses” by Jennifer Kennedy.
- Calumpong, H. and Menez, E. 1997. Field Guide to Common Mangroves, Seagrasses and Algae of the Philippines. The Philippines: The Bookmark, Inc. 197 p. ISBN# 971-569-197-8.
