Kuala Lumpur, 23 October 2025 — The afternoon session of the Great Innovation Challenge (GIC) 2025: Reengineering Plastic for Impact continued with a highly technical and engaging workshop focusing on 3D modelling, digital rendering, microcontroller integration, and IoT automation.
Organised by the Centre for Artificial Intelligence & Robotics (CAIRO), Universiti Teknologi Malaysia (UTM), in collaboration with the IEEE Kuala Lumpur Subsection, the session was proudly sponsored by Great Eastern Takaful Berhad (GETB).
![]() Technical Highlights (Session 2)
Technical Highlights (Session 2)
Trainers: Mr. Zaenal Abidin & Mr. Thaqif Iman
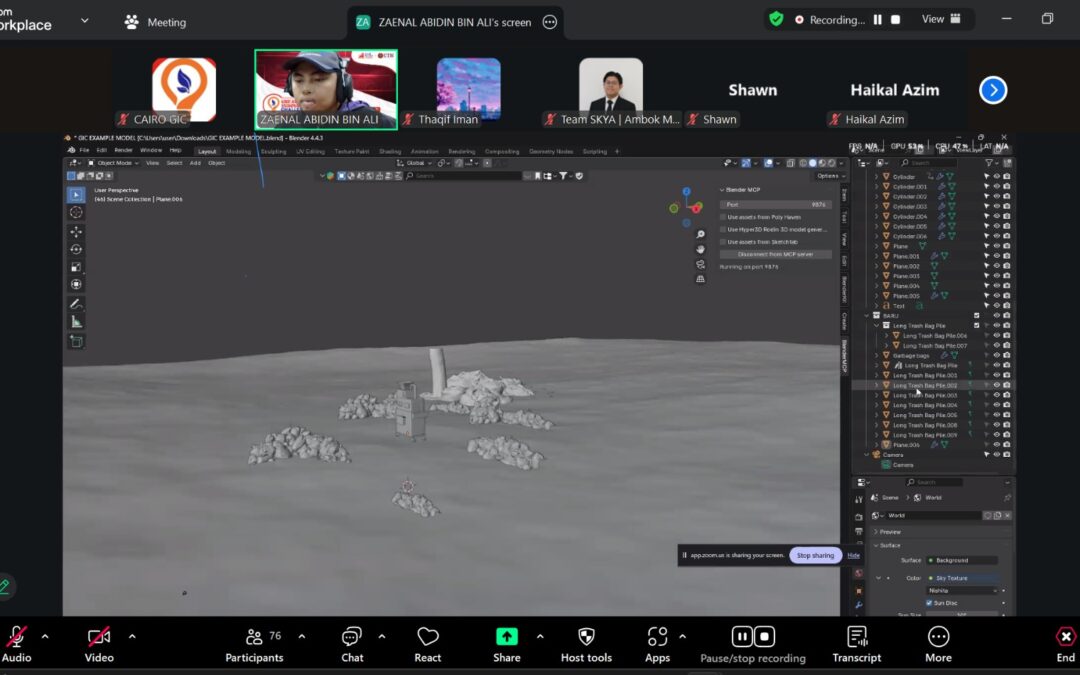
![]() 3D Modelling & Rendering with Blender and SolidWorks
3D Modelling & Rendering with Blender and SolidWorks
Led by Mr. Zaenal Abidin, participants explored how to transform design concepts into realistic 3D models that can be used for simulation and presentation.
Key takeaways included:
– Understanding mesh, surface, and object structures in 3D design.
– Exporting models in STL, OBJ, and USD formats for 3D printing or simulation.
– Applying materials, lighting, and camera effects for high-quality rendering.
– Emphasising modular, portable, and robust design for small-scale recycling systems.
– Using AI-based image generation tools to conceptualise machine layouts and improve design creativity.
This hands-on module helped students visualise their machine ideas more clearly and professionally before entering the prototyping stage.
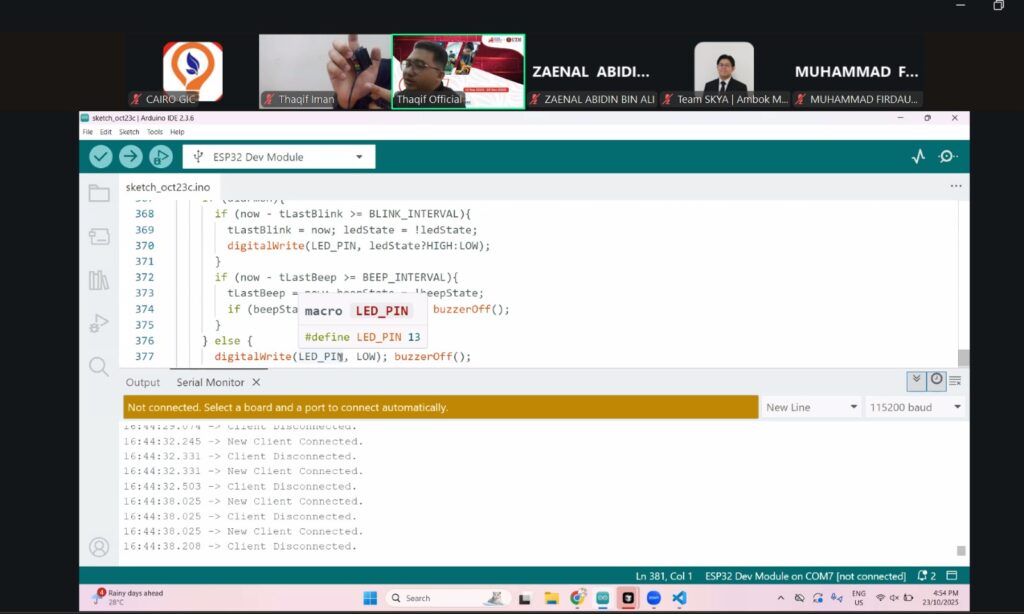
![]() Microcontroller Integration & IoT Dashboard Development
Microcontroller Integration & IoT Dashboard Development
The second part of the session, conducted by Mr. Thaqif Iman, guided participants into the world of electronics, control systems, and smart automation.
Key learning areas included:
– Basics of sensors, actuators, and ESP32 microcontrollers.
– Power and safety design using relays, MOSFETs, SSRs, and fuses.
– Developing a local IoT dashboard to monitor temperature, motor activity, and system status.
– Introduction to AI-assisted development and edge computing, showcasing how tools like ChatGPT and GitHub Copilot can accelerate circuit design, debugging, and code generation.
Participants also experimented with simulation tools such as Tinkercad to test their circuits virtually before hardware implementation, reinforcing safe and efficient prototyping practices.
![]() Hands-On Learning in Action
Hands-On Learning in Action
– Both trainers demonstrated step-by-step processes for:
– Building and exporting 3D models for virtual simulation.
– Writing and uploading Arduino IDE code for ESP32 boards.
– Hosting a custom IoT dashboard within the controller for local monitoring.
– Integrating the design logic between the mechanical and electronic subsystems.
The interactive format encouraged teams to test, refine, and discuss their ideas in real-time — embodying the innovation-driven spirit of GIC 2025.
![]() Key Learning Outcomes
Key Learning Outcomes
Participants learned how to design and render 3D models effectively.
Teams gained practical experience in microcontroller programming and IoT integration.
The workshop bridged mechanical, electronic, and digital design principles.
Participants were introduced to AI-driven workflows that enhance efficiency and creativity.
![]() Conclusion
Conclusion
The Day 1 Session 2 Workshop marked a productive and inspiring continuation of the Great Innovation Challenge 2025.
Through a combination of 3D modelling, IoT automation, and AI-assisted development, participants are now equipped with the knowledge and tools to bring their sustainable recycling machine concepts to life.
This session reinforced GIC’s vision — to empower youth to create innovative, smart, and sustainable engineering solutions that drive real-world impact. ![]()
![]() Suggested Visuals for Post
Suggested Visuals for Post
3D model screenshots (Blender/SolidWorks).
ESP32 setup with sensors and dashboard display.
Team snapshots or Zoom session gallery.
![]() Stay Connected
Stay Connected
![]() Official Website: research.utm.my/cairo/greatinnovationchallenge
Official Website: research.utm.my/cairo/greatinnovationchallenge


Recent Comments